
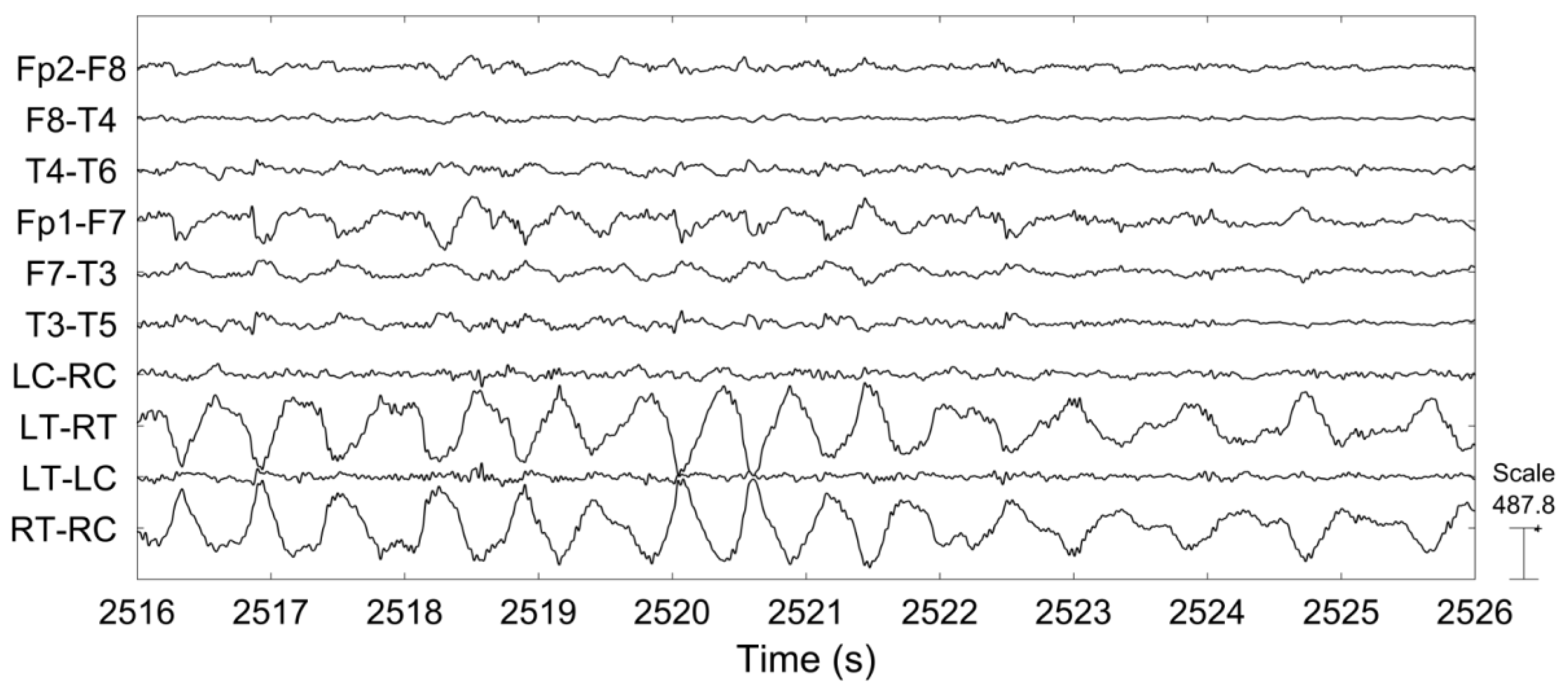
The left temporal discharge above, for example, has a good field throughout the left temporal region, with the surrounding tracings "pointing to" the discharge site, as expected in bipolar montages. Whether an interictal has an appreciable slow wave or not, it should always disrupt the background and have a field this is to say, you should see "ripples" of a discharge in the surrounding EEG electrodes (as discussed in the technical section). Slow waves always immediately follow, and are often higher amplitude than, their precedent spikes or sharps. Realistically, the cutoff between them is not very important clinically, as one isn't known to be any more "severe" than the other.Īfter a spike or sharp, there is typically a slow wave, which represents the refractory period of the affected neuron population after the large and synchronized EPSPs that led to the spike or sharp itself. A spike is very similar to a sharp but faster, with a duration from 20-70ms. A sharp is a single epileptiform discharge defined by its duration lasting between 70-200ms, and by its disruption of the EEG background. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry JournalAny epileptiform discharge is a disruption of the usual functioning of the brain, and sharps and spikes are perhaps the most classic type.119999 - MEDICAL AND HEALTH SCIENCES NOT ELSEWHERE CLASSIFIED.The outcomes of an abnormal EEG may or may not change the treatment.


We aim to present the findings of the paper.Ĭonclusions: EEG is an important investigation and should be used cautiously. We then did a literature search on the topic. Of the two categories, we then analysed the data and asked the above questions. We reviewed the EEG findings of these patients. Methods/findings: We reviewed all the records of the patients presented to Mirrabook Jan.–Dec. If the findings are abnormal, then what does it mean? What else do we do? Should we do EEG routinely? We aim to answer these questions in our paper. Objectives: If the findings are normal, we may not do anything. The distinction from organic to functional is vague and probably need further clarification. It helps to differentiate the organic from functional disorders. EEG helps to unlock or diagnose underlying organic issue and helps to share light on the future prognosis of the patient. Background: Electroencephalogram (EEG) is commonly or uncommonly used in daily clinical practice.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
